Buffer Area Chemistry Definition
A buffer zone in chemistry is a region where the pH of a solution remains constant. A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions.
 Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons.

Buffer area chemistry definition. Buffer zones also exist with weak bases and strong acids. Chapter I -- Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Department of Agriculture buffer area means that area in a primary enclosure for a swim-with-the-dolphin program that is off-limits to members of the public and that directly abuts. Acidic solutions contain high concentrations of hydrogen ions H and have pH values less.
Here we are going to learn about buffer capacity chemistry definition and formula. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration. The walls floors ceilings and all surfaces must be smooth and easy to clean and only a minimal amount of furniture may remain in the room.
In this way a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate. A buffer room must be kept sterile at all times.
All workers entering the buffer room must wear a face mask and apron to protect the immediate area from their germs. What Is a Buffer. 49 votes See 1 more reply.
The chemical composition of a buffer solution usually entails a weak acid or a weak base accompanied by its conjugate salt. The buffer capacity can also be defined as the amount of mole of strong base needed to change the pH of 1 L of solution by 1 pH of unit. In water solution sodium acetate is completely dissociated into sodium Na and acetate CH 3 COO - ions.
A buffer is a solution that can maintain a nearly constant pH if it is diluted or if relatively small amounts of strong acids or bases are added. A buffer solution can be made by mixing a weak acid with one of its salts OR mixing a weak base with one of its salts. Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base.
This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. How are Acid-Base Buffers Made. In an acid-base titration of a weak acid with a strong base the pH of the solution increases levels off through the buffer zone and then increases quickly to reach the equivalence point.
Chemistry A substance that prevents change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution. There are two key terms associated with buffers. A buffer system is a solution that resists a change in pH when acids or bases are added to it.
Buffers are used to maintain a stable pH in a solution as they can neutralize small quantities of additional acid of base. For example the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood. Buffers are characterized by the pH range over which they can maintain a more or less constant pH and by their buffer capacity the amount of strong acid or base that can be absorbed before the pH changes significantly.
Similarly adding water to a buffer or allowing water to evaporate will not change the pH of a buffer. Buffer Area Law and Legal Definition According to 9 CFR 11 Title 9 -- Animals and Animal Products. Search buffer area and thousands of other words in English definition and synonym dictionary from Reverso.
Now Buffer Capacity can be defined as the measure of the efficiency of a buffer in resisting its change in pH. The buffer room is the only absolutely sterile room in the pharmacy. According to the USDA organic regulations a buffer zone is an area located between a certified production operation or portion of a production operation and an adjacent land area that is not maintained under organic management.
If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly. In nature there are many systems that use buffering for pH regulation. A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa.
In practice a buffer solution contains either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The higher the acid concentration of the buffer then the buffer capacity will be higher as well. A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base.
The buffer capacity is a quantity in resisting the pH change at the time of addition of an acid or base. By definition a buffer system is a solution that resists a change in pH when acids or bases are added. Buffer area or cleanroom means a room or area where the primary engineering control device is physically located and in which the concentration of airborne particles is controlled to meet a specified airborne particulate cleanliness class.
A buffer may also be called a pH buffer hydrogen ion buffer or buffer solution. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH.
In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Computer Science A device or an area of a computer that temporarily stores data that is being transferred between two machines that process data at different rates such as a computer and a printer. A buffer is a compound that resists changes in pH when a limited amount of acid or base is added to it.
In order for the pharmacy to remain up to code it must stay this way. You can complete the definition of buffer area given by the English Definition dictionary with other English dictionaries. Wikipedia Lexilogos Oxford Cambridge Chambers Harrap Wordreference Collins Lexibase dictionaries Merriam Webster.
It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications.
 Best Chemistry Blogs Making Chemistry Easy Tips And Tricks What Is Buffer Solution Buffer Solution Chemistry Classroom Electron Configuration
Best Chemistry Blogs Making Chemistry Easy Tips And Tricks What Is Buffer Solution Buffer Solution Chemistry Classroom Electron Configuration
 Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
 Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is Valency In Chemistry Definition Example 11th Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry
Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is Valency In Chemistry Definition Example 11th Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Buffers And Henderson Hasselbalch Chemistry Khan Academy Khan Academy Chemistry Henderson
Buffers And Henderson Hasselbalch Chemistry Khan Academy Khan Academy Chemistry Henderson
 Buffer Solutions Math Methods Buffer Solution Mental Math
Buffer Solutions Math Methods Buffer Solution Mental Math
 Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs Sodium Chloride Electrolysis Half Reactions Oxid Chemistry Redox Reactions Informative
Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs Sodium Chloride Electrolysis Half Reactions Oxid Chemistry Redox Reactions Informative
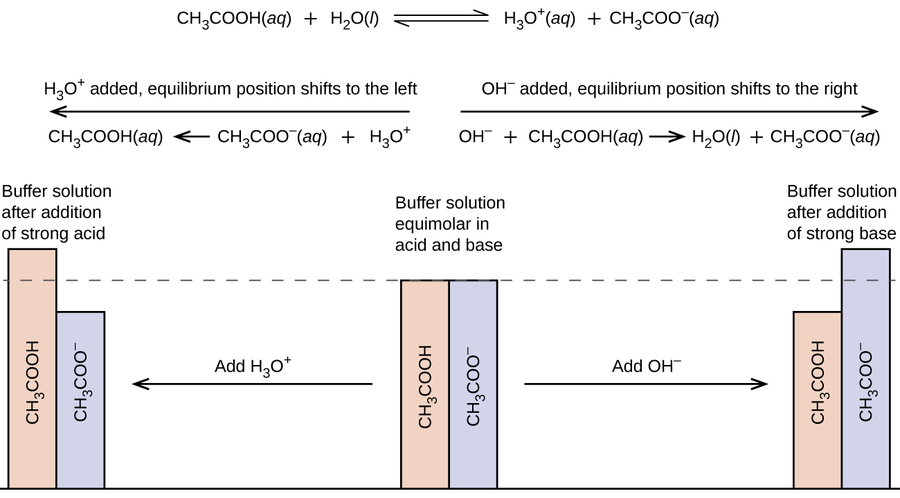 7 1 Acid Base Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
7 1 Acid Base Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 Buffer Solutions Buffer Solution Fun Learning Ap Chemistry
Buffer Solutions Buffer Solution Fun Learning Ap Chemistry
Buffers Indicators Acids And Bases 101 The Basics Of Chemistry
 What Is Electrolytic Cell Cell Definition Cell Chemistry
What Is Electrolytic Cell Cell Definition Cell Chemistry
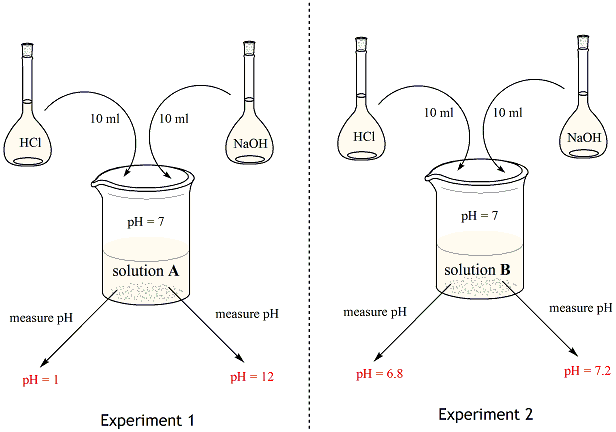 Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
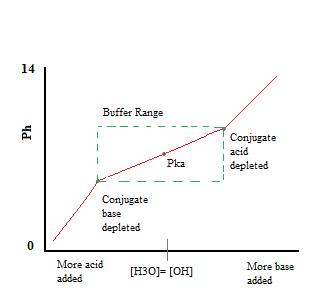 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 Buffer Capacity Buffers Titrations And Solubility Equilibria Chemi Solubility Chemistry Ap Chemistry
Buffer Capacity Buffers Titrations And Solubility Equilibria Chemi Solubility Chemistry Ap Chemistry

