Buffer Zone Definition Chemistry
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. Meaning pronunciation translations and examples.
 Hydrogen Bonding Definition Examples And Types Digital Kemistry Hydrogen Bond Bond Molecules
Hydrogen Bonding Definition Examples And Types Digital Kemistry Hydrogen Bond Bond Molecules
An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate.

Buffer zone definition chemistry. In an acid-base titration of a weak acid with a strong base the pH of the solution increases levels off through the buffer zone and then increases quickly to reach the equivalence point. A solution which can maintain an almost constant pH value when dilute acids or alkalis are added to it. Buffers are used to make solutions of known pH especially for instrument calibration purposes.
According to the USDA organic regulations a buffer zone is an area located between a certified production operation or portion of a production operation and an adjacent land area that is not maintained under organic management. Similarly adding water to a buffer or. Anne Marie Helmenstine PhD.
A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versaIts pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. The midpoint of the buffering region is when one-half of the acid reacts to dissociation and where the concentration of the proton donor acid equals that of the proton acceptor base. A buffer zone is generally a zonal area that lies between two or more other areas but depending on the type of buffer zone the reason for it may be to segregate regions or to conjoin them.
This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. See the full definition for buffer zone in the English Language Learners Dictionary. The buffering region is about 1 pH unit on either side of the pK a of the conjugate acid.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. Also called area of separation in some United Nations operations. Common types of buffer zones are demilitarized zones border zones and certain restrictive easement zones and green belts.
A buffer zone must be sufficient in size or. A buffer is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which is resistant to changes in pH. Buffer bŭf ər Chemistry A substance that prevents change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution or when the solution is diluted.
This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. In water solution sodium acetate is completely dissociated into sodium Na and acetate CH 3 COO - ions.
English Language Learners Definition of buffer zone. There are two key terms associated with buffers. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration.
A buffer zone is formed to create an area of separation between disputing or belligerent forces and reduce the risk of renewed conflict. A defined area controlled by a peace operations force from which disputing or belligerent forces have been excluded. Updated May 04 2019.
In chemistry buffer solution and examplesIt is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which resists changes in pH. Noun a neutral zone or area between two potentially hostile nations designed to prevent any overt acts of aggression. Common types of buffer zones are demilitarized zones border zones and certain restrictive easement zones and green belts.
A buffer is a compound that resists changes in pH when a limited amount of acid or base is added to it. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. A buffer zone is a neutral zonal area that lies between two or more bodies of land usually pertaining to countries.
Now Buffer Capacity can be defined as the measure of the efficiency of a buffer in resisting its change in pH. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. A buffer zone is an area created to separate opposing forces or groups which belongs to.
Buffer chemistry synonyms Buffer chemistry pronunciation Buffer chemistry translation English dictionary definition of Buffer chemistry. What is a buffer zone. Buffer zones also exist with weak bases and strong acids.
A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pHA buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base. An area that keeps two things separated. A buffer zone in chemistry is a region where the pH of a solution remains constant.
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly. 7 CFR 2052.
Depending on the type of buffer zone it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them. In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable.
What Is a Buffer. Any area serving to mitigate or neutralize potential conflict. The chemical composition of a buffer solution usually entails a weak acid or a weak base accompanied by its conjugate salt.
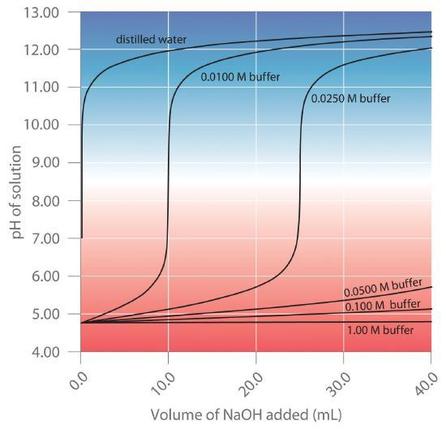 8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
 Chapter 16 6 Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Chapter 16 6 Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Titrations Acid Base Titrations Sparknotes
 Electrolytic Cell Chemistry Cell Definition Chemistry Lessons Chemistry
Electrolytic Cell Chemistry Cell Definition Chemistry Lessons Chemistry
 Isotope Definition Types And Examples Chemistry Basics Chemistry Science Student
Isotope Definition Types And Examples Chemistry Basics Chemistry Science Student
 The Sources And Impacts Of Water Pollution Water Pollution Pollution Activities What Is Water
The Sources And Impacts Of Water Pollution Water Pollution Pollution Activities What Is Water
 Proglottid Science Flashcards Science Facts Science Student
Proglottid Science Flashcards Science Facts Science Student
 Buffer Effectiveness Boundless Chemistry
Buffer Effectiveness Boundless Chemistry
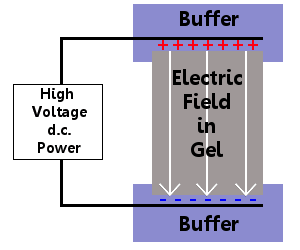 Definition Of Electrophoresis Chemistry Dictionary
Definition Of Electrophoresis Chemistry Dictionary
 What Is Causing The Buffer Region In A Weak Acid Strong Base Titration Chemistry Stack Exchange
What Is Causing The Buffer Region In A Weak Acid Strong Base Titration Chemistry Stack Exchange
Buffers Indicators Acids And Bases 101 The Basics Of Chemistry
 2 Opec Includes 12 Members On 3 Continents The Founding Members 1960 Are Venezuela Iran Iraq Saudi Arabia An History Projects Libya United Arab Emirates
2 Opec Includes 12 Members On 3 Continents The Founding Members 1960 Are Venezuela Iran Iraq Saudi Arabia An History Projects Libya United Arab Emirates
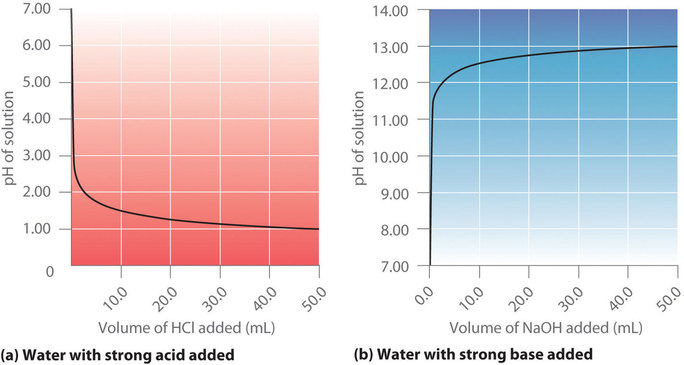 7 3 Acid Base Titrations Chemistry Libretexts
7 3 Acid Base Titrations Chemistry Libretexts
 Buffer Zone An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Buffer Zone An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 What Is Buffer Zone What Does Buffer Zone Mean Buffer Zone Meaning Definition Explanation Youtube
What Is Buffer Zone What Does Buffer Zone Mean Buffer Zone Meaning Definition Explanation Youtube
 Diagram Of Protein Electrophoresis Workflow Study Biology Clinical Chemistry Microbiology Study
Diagram Of Protein Electrophoresis Workflow Study Biology Clinical Chemistry Microbiology Study
