Buffer Solution Meaning Biology
A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. Consisting mostly of water.
 Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs Why Are Bond Angles Of H2o Nh3 104 5 And 107 5 Chemistry Bond Simple Words
Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs Why Are Bond Angles Of H2o Nh3 104 5 And 107 5 Chemistry Bond Simple Words
An example of a buffer solution is bicarbonate in blood which maintains the bodys internal pH.

Buffer solution meaning biology. Acidic buffer solutions are those that have strong acids and weak bases as their components. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes. Prepare 1 liter of 1X TBE buffer from a 10X TBE stock solution.
Biological Importance of Buffers. In this way a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally. They help in a neutralization reaction to a certain extent.
Such concentrated stocks take up less space. A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base. It is a water-based salt solution containing disodium hydrogen phosphate sodium chloride and in some formulations potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate.
DEFINITION A buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid its salt or a weak base its salt that resist a change in pH on the addition of either acid or base. A buffer is a mixture of an acid that does not ionize completely in water and its corresponding base-for example carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and sodium bicarbonate NaHCO 3. In order to save time and space molecular biologists often make concentrated stocks of solutions to last over long periods of time.
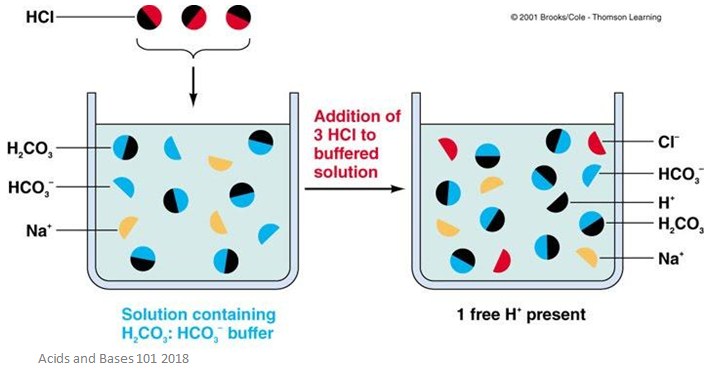
In nature there are many systems that use buffering for pH regulation. Buffer Solution is a water solvent based solution which consists of a mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base. The bicarbonate buffer neutralizes stronger dietary and metabolic acids HA converting them into weak bases A with the increase in H 2 CO 3.
Buffers typically consist of an acid-base pair with the acid and base differing by the presence or absence of a proton a conjugate acid-base pair. For example the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes.
Note- A lot of biological chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. This solution is quite important in the field of chemistry.
You can explore more about buffer solutions here. A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH. A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed.
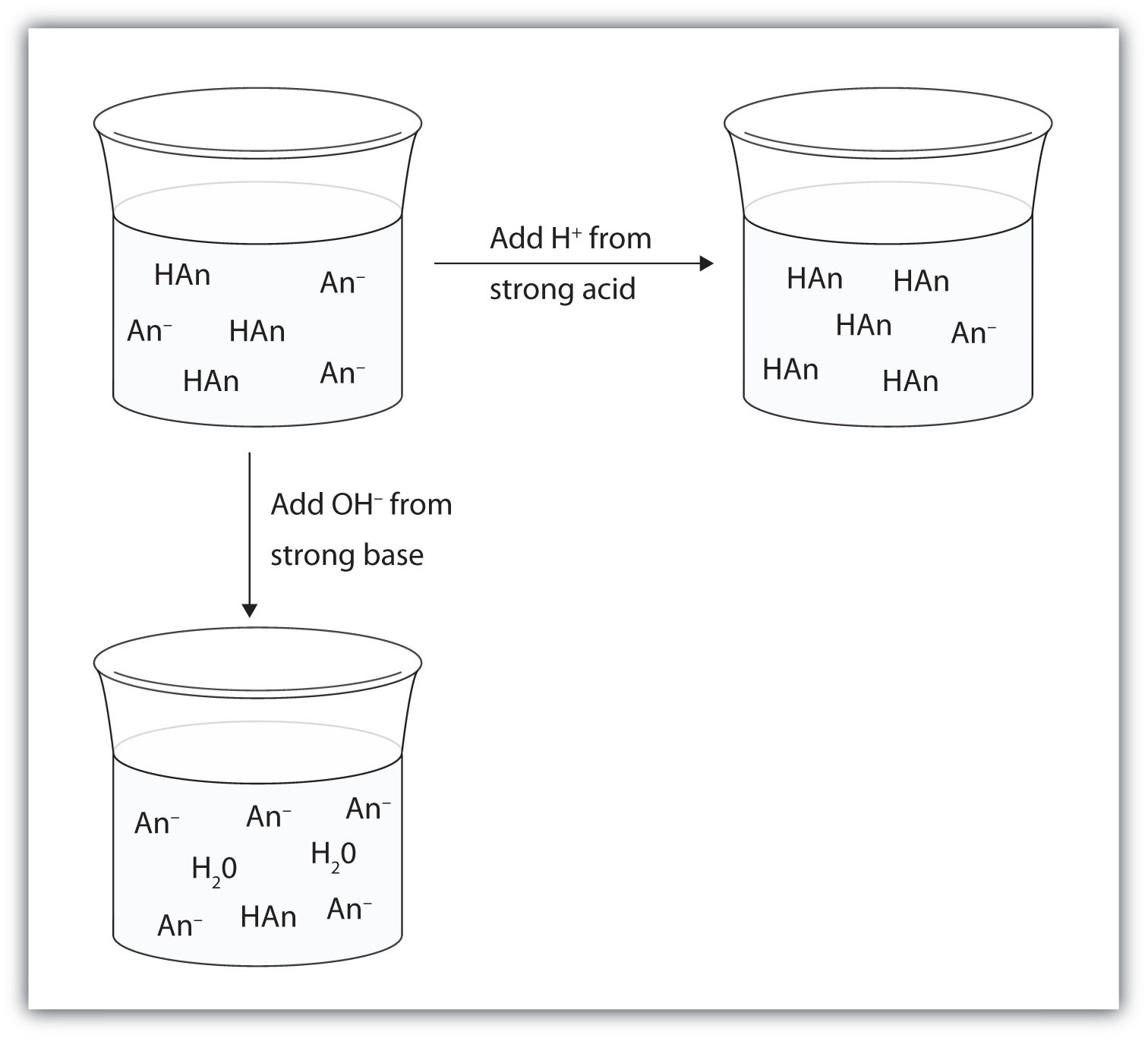
If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly. Buffer solutions are solutions in water that mark the combination of acids and bases. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
Furthermore it consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice-versa. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it and is thus used to prevent a solution s pH change.
Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant. Buffers are extremely useful in these systems to maintain the pH at a constant value.
A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions. A buffer is an aqueous solution that consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its salt acid buffer or a weak base with its salt basic buffer. Buffers are solutions that resist a change in pH on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali.
Buffer solutions are necessary in biology for keeping the correct pH for proteins to work. 1 chemistry A buffer solution. An example of a.
Define Buffer Solution Biology A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant. In a molecular biology research lab you will constantly need to make and use buffers. Buffers can be prepared in multiple ways by creating a solution of an acid and its conjugate base.
This does not mean that the pH of buffers does not change. The buffer helps to maintain a constant pH. A buffer solution refers to an aqueous solution.
It is the main buffer in blood plasma and consists of bicarbonate HCO 3 and carbonic acid H 2 CO 3. They resist a change in pH upon dilution or upon the addition of small amounts of acidalkali to them. For instance one of the buffers that maintain the pH of human blood involves carbonic acid H.
A buffer system has the property of resisting pH changes despite additions of acid or base. Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base. Meaning of Buffer System.
Phosphate-buffered saline abbreviated PBS is a buffer solution commonly used in biological research. A solution containing either a weak acid and a conjugate base or a weak base and a conjugate acid used to stabilize the pH of a liquid upon dilution. If acid is added to this buffer the added H ions combine with bicarbonate ions to produce more carbonic acid using up some of the H ions the Na ions do not participate in this reaction.
 Acid Base Buffers Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision
Acid Base Buffers Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision
 What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
 Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is Valency In Chemistry Definition Example 11th Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry
Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is Valency In Chemistry Definition Example 11th Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry
 Best Chemistry Blogs Reactions Of Aldehyde Ketone With Hcn Nahso3 Ald Reactions Aldol Condensation Ketones
Best Chemistry Blogs Reactions Of Aldehyde Ketone With Hcn Nahso3 Ald Reactions Aldol Condensation Ketones
 10 5 Buffers The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry
10 5 Buffers The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry
 Common Ion Effect Animation Chemistry Ionic Equilibrium
Common Ion Effect Animation Chemistry Ionic Equilibrium
 Allotropy And Polymorphism Crystalline Solid Class Trick
Allotropy And Polymorphism Crystalline Solid Class Trick
 The Body S Buffer System And Ph Imbalances Helpful Youtube Video Nursing School Notes Respiratory Therapy Medical Laboratory Scientist
The Body S Buffer System And Ph Imbalances Helpful Youtube Video Nursing School Notes Respiratory Therapy Medical Laboratory Scientist
 Foundations Of Molecular Cloning Past Present And Future Biochemistry Notes Molecular Microbiology
Foundations Of Molecular Cloning Past Present And Future Biochemistry Notes Molecular Microbiology
 Types Of Hydrogen Isotopes Chemistry Basics Science Chemistry Chemistry
Types Of Hydrogen Isotopes Chemistry Basics Science Chemistry Chemistry
 Acids And Bases Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Review Science Notes
Acids And Bases Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Review Science Notes
 Buffer Solutions Chemistry Review Buffer Solution Chemistry
Buffer Solutions Chemistry Review Buffer Solution Chemistry
 Why Isotopes Are Unstable Chemistry Basics Chemistry Science Student
Why Isotopes Are Unstable Chemistry Basics Chemistry Science Student
 Acids Bases Draw It To Know It Study Chemistry Chemistry Education Biochemistry Notes
Acids Bases Draw It To Know It Study Chemistry Chemistry Education Biochemistry Notes
 This Video Is First Part Of Uv Spectroscopy It Covers Electromagnetic Spectrum Beer La Teaching Chemistry Electromagnetic Spectrum Medical Laboratory Science
This Video Is First Part Of Uv Spectroscopy It Covers Electromagnetic Spectrum Beer La Teaching Chemistry Electromagnetic Spectrum Medical Laboratory Science



